@#8 ... Measles kills about a few hundred people a year. ...
Currently.
... You know what's funny? Obesity kills nearly 300,000 of you purple-haired pronoun- nose ring wearing ----- every year.. ...
I do not consider the deaths of Americans to be funny in any shape manner or form.
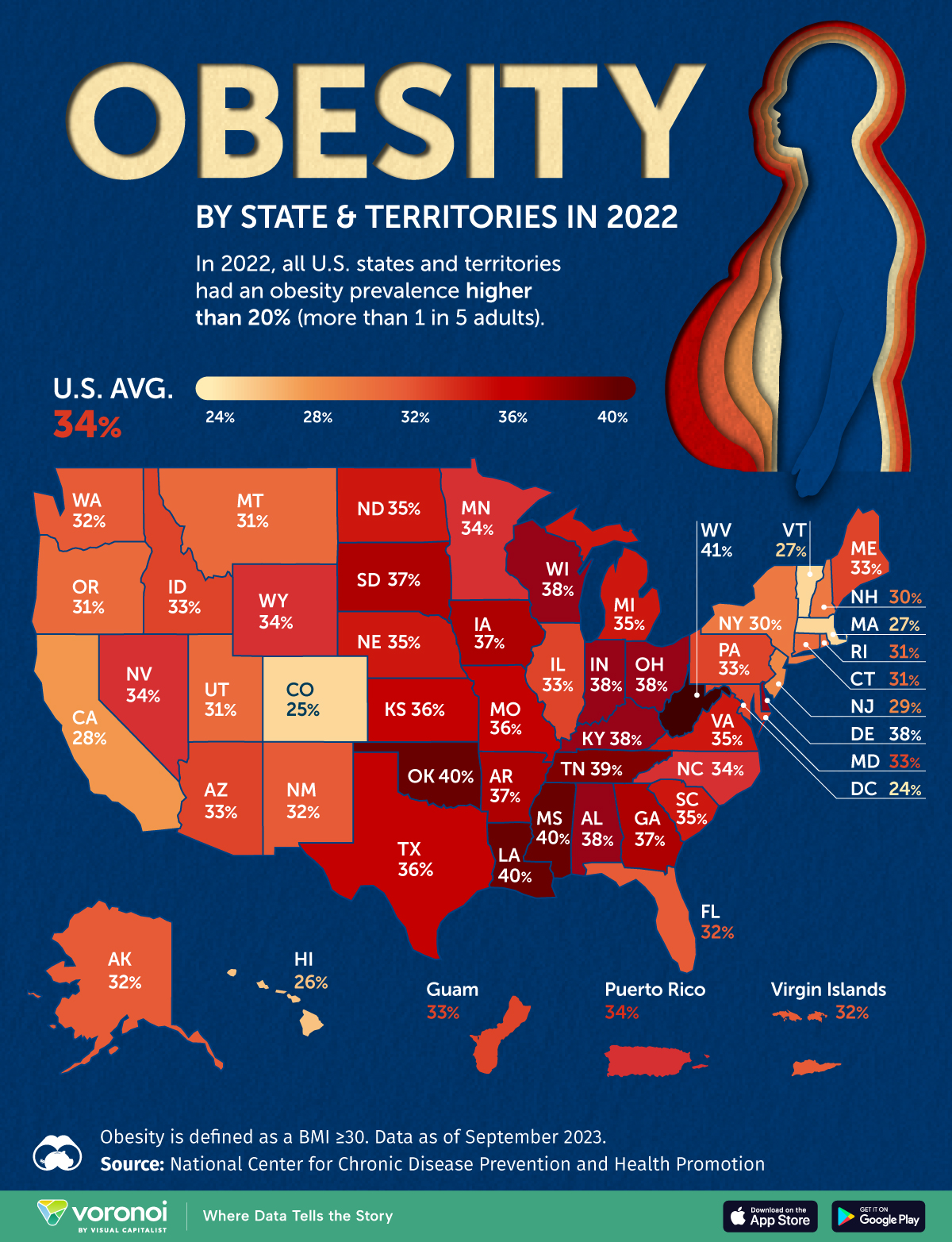
Mapped: U.S. Obesity Rates, by State (August 2024)
https://www.visualcapitalist.com/mapped-u-s-obesity-rates-by-state/
Excerpt ...